Serving San Antonio's Industrial Needs:
Bohls Equipment
BEARINGS
Home of the Largest Inventory in Central and South Texas
Bearings
Reliable Ball Bearings in Austin, Laredo, Victoria & San Antonio, TX
We carry the best bearings in the state of Texas. If you're in the San Antonio, Austin, Laredo, or Victoria, TX
areas, stop into our storefront to see what we have in stock. If you have any questions about bearings, we would be happy to assist. Give us a call today
to speak to a member of our team.
Take a look at our selection of bearings, which includes the following:
Ball Bearings
Overview
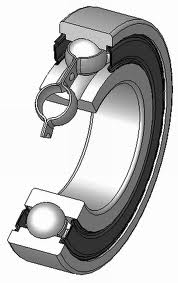
Ball bearings are rolling-element bearings that uses balls to maintain the separation between the bearing races.
The ball bearing reduces rotational friction and supports radial and axial loads by using at least two races to contain the balls and transmit the loads through the balls. In most applications, one race is stationary while the other is attached to the rotating assembly, like a hub or shaft.
Tapered Roller Bearings
Overview
Tapered roller bearings are uniquely designed to manage both thrust and radial loads on rotating shafts and in housings.

Features
Tapered roller bearings consist of four interdependent components: the cone, or inner ring; the cup, or outer ring; the tapered rollers, or rolling elements; and the cage, or roller retainer. The taper angles allow the bearing to handle a combination of radial and thrust loads. The steeper the cup angle, the greater the ability of the tapered roller bearing to handle thrust loads.
Cylindrical Roller Bearing
Overview
Cylindrical bearings provide the highest possible radial load capacity compared to other roller bearing types. Four primary styles are available to meet a variety of application requirements.

Spherical Roller Bearing
Overview
This type of bearing permits angular rotation in two orthogonal directions about a central point (based on the bearing geometry). The bearings typically support a rotating shaft in the inner ring bore, moving rotationally at an angle.

Features
These bearings are used in applications where rotational motion is needed to change the alignment of the rotation axis, like in the drive axle bearings of a vehicle control arm suspension. This allows the axle to move up and down while the axle bearings allow the rotational axis to change without binding. While in practice, spherical bearings are not used here, it is a simple concept that illustrates a possible application of a spherical bearing. In fact, spherical bearings are used in smaller sub-components like certain constant-velocity joints.
Spherical bearings are used in car suspensions, engines, drive-shafts, heavy machinery, sewing machines, and many other applications.
Features
Angular Contact
Angular contact ball bearings use axially asymmetric races. An axial load passes in a straight line through the bearing, whereas a radial load takes an oblique path that tends to want to separate the races axially. This means the angle of contact on the inner race is the same as that on the outer race. Angular contact bearings better support "combined loads" (loading in both the radial and axial directions) and the contact angle of the bearing should be matched to the relative proportions of each.
Deep-Groove
In a deep-groove radial bearing, the race dimensions are close to the dimensions of the balls that run in it. Deep-groove bearings can support higher loads.
Needle Roller Bearing
Overview
A needle roller bearing is a bearing which uses small cylindrical needles to reduce friction of a rotating surface.

Features
Needle bearings have a large surface area that is in contact with the bearing outer surfaces compared to ball bearings. Additionally, there is less added clearance (difference between the diameter of the shaft and the diameter of the bearing), so they are much more compact. The typical structure consists of a needle cage which orients and contains the needle rollers, the needle rollers themselves, and an outer race (sometimes housing itself).
Radial needle bearings are cylindrical and use rollers parallel to the axis of the shaft. Thrust needle bearings are flat and use a radial pattern of needles.
Full complement bearings have solid inner and outer rings and rib-guided cylindrical rollers. Since these bearings have the largest possible number of rolling elements, they have extremely high radial load carrying capacity and are suitable for particularly compact designs.
Proudly Serving Southern Texas
If ball bearings are essential to getting your job done, turn to Bohls Equipment to find what you need. We have a massive selection of ball bearings and all the other industrial parts you need to complete the job. Our selection of industrial parts includes electric motors, V-belts, sheaves, roller chains, chain sprockets, oil and grease seals, hydraulic hoses, hydraulic fittings, conveyor belts, and more. Contact us today to place an order for bearings and equipment you need. We have the finest selection of industrial parts in San Antonio, TX; Austin, TX; Laredo, TX; and Victoria, TX.
